SEO Best Practices for Web Developers: Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is crucial for the success of any website. As a web developer, integrating SEO best practices from the ground up ensures that the websites you build are optimized for search engines, leading to better visibility and higher rankings in search results. This comprehensive guide covers the essential SEO practices every web developer should follow to create search-engine-friendly websites.
Understanding SEO Best Practices for Web Developers
Before diving into specific practices, it’s essential to understand what SEO is and why it matters.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) improves a website’s visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs). The goal is to attract organic (non-paid) traffic by ensuring the website appears higher in search results for relevant queries. Effective SEO involves a combination of on-page optimization, technical SEO, and content strategies.

SEO-Friendly URL Structure
URLs are among the first things search engines look at when crawling a website. A well-structured URL can help search engines understand a page’s content and improve user experience.
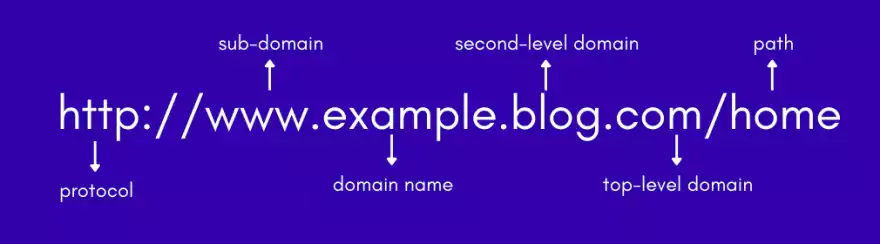
Best Practices for URL Structure
- Use Clean and Descriptive URLs: Avoid using complex and lengthy URLs. Instead, use simple and descriptive URLs that give users and search engines a clear idea of the page content.
- Example: https://example.com/seo-best-practices
- Include Keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords into the URL to enhance its SEO value.
- Example: https://example.com/web-development-seo
- Use Hyphens to Separate Words: Hyphens improve readability for users and search engines.
- Example: https://example.com/seo-tips
- Avoid Special Characters and Numbers: These can confuse users and search engines.
- Bad Example: https://example.com/page?id=12345
On-Page SEO Elements
On-page SEO involves optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic. Key on-page elements include titles, meta descriptions, headings, and images.

Title Tags
Title tags are one of the most important on-page SEO factors. They appear in search engine results and influence click-through rates.
- Keep Titles Under 60 Characters: This ensures they display correctly in SERPs.
- Include Primary Keywords: Place primary keywords at the beginning of the title.
- Write Unique Titles: Each page should have a unique title that accurately reflects its content.
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions provide a summary of a page’s content. While they don’t directly affect rankings, they can influence click-through rates.
- Keep Meta Descriptions Under 160 Characters: This prevents them from being cut off in search results.
- Include Keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords naturally.
- Write Compelling Descriptions: Encourage users to click through to the page.
Headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.)
Headings structure the content on a page, making it easier for users and search engines to understand.
- Use One H1 Tag per Page: This should represent the page’s main topic.
- Include Keywords in Headings: Naturally integrate keywords into H2 and H3 tags.
- Maintain a Logical Hierarchy: Ensure headings follow a logical order (H1, H2, H3, etc.).
Image Optimization
Images enhance user experience but need to be optimized for SEO.
- Use Descriptive File Names: Include keywords in image file names.
- Example: SEO-best-practices.jpg
- Add Alt Text: Describe the image content with relevant keywords to help search engines understand the image.
- Compress Images: Reduce file sizes to improve page load speed without sacrificing quality.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO improves a website’s backend structure to enhance its visibility and performance in search engines.

XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap lists all the pages on your website, helping search engines crawl and index them efficiently.
- Create an XML Sitemap: Use tools or plugins to generate an XML sitemap.
- Submit Sitemap to Search Engines: Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
Robots.txt
The robots.txt file instructs search engines which pages to crawl and index.
- Create a Robots.txt File: Ensure it is correctly configured to allow search engines to crawl essential pages.
- Block Unimportant Pages: Prevent search engines from indexing duplicate or low-value pages.
SSL Certificates
Security is a ranking factor for search engines. Ensure your website uses HTTPS.
- Implement SSL Certificates: Obtain and install an SSL certificate to secure your website.
- Redirect HTTP to HTTPS: Ensure all traffic is redirected to the HTTPS version of your site.
Website Speed and Performance
Website speed is crucial for both user experience and SEO. Slow-loading websites can negatively impact search rankings and user engagement.
Best Practices for Improving Speed
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Reduce the number of elements on your page (scripts, images, etc.) to decrease load time.
- Enable Compression: Use tools like Gzip to compress files and reduce their size.
- Optimize CSS and JavaScript: Minify CSS and JavaScript files to remove unnecessary characters and reduce file size.
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs distribute your content across multiple servers, reducing load times for users worldwide.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Set expiration dates for static resources to reduce load times for returning visitors.
Mobile Optimization
With the increasing use of mobile devices, optimizing websites for mobile is essential. Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it predominantly uses the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking.
Best Practices for Mobile Optimization
- Responsive Design: Use responsive web design to ensure your site adapts to different screen sizes and devices.
- Optimize for Touch: Ensure buttons and links are easily clickable on touch screens.
- Improve Load Times: Mobile users expect fast load times, so focus on optimizing speed for mobile devices.
- Test Mobile Usability: Use tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to identify and fix mobile usability issues.
Content Optimization
High-quality, relevant content is the backbone of SEO. Search engines aim to deliver the best possible content to users.
Keyword Research
Effective SEO starts with thorough keyword research.
- Identify Relevant Keywords: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to find keywords relevant to your audience.
- Analyze Competitors: Study competitor websites to identify keywords they are targeting.
- Focus on Long-Tail Keywords: Long-tail keywords are less competitive and often more specific, leading to higher conversion rates.
Content Creation
Once you have your keywords, integrate them naturally into your content.
- Write High-Quality Content: Focus on providing valuable information that addresses the needs and questions of your audience.
- Use Keywords Naturally: Avoid keyword stuffing; incorporate keywords naturally throughout the content.
- Include Multimedia: Use images, videos, and infographics to enhance content and engage users.
- Update Content Regularly: Keep your content fresh and up-to-date to maintain relevance.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
Structured data helps search engines understand the content on your website and provide richer search results.
Implementing Schema Markup
- Identify Relevant Schema Types: Use schema types relevant to your content (e.g., articles, products, events).
- Add Schema Markup: Use tools like Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper to generate and implement schema markup.
- Test Structured Data: Use Google’s Rich Results Test to implement your structured data correctly.
Internal Linking
Internal linking helps search engines understand the structure of your website and discover new pages.
Best Practices for Internal Linking
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text: Use relevant keywords in the anchor text to describe the linked page.
- Link to Relevant Pages: Ensure that the internal links are relevant to the content and provide additional value to the user.
- Create a Logical Structure: Organize your website’s content logically and use internal linking to reflect this structure.
Monitoring and Analytics
Monitoring your website’s performance is crucial to understanding your SEO efforts’ effectiveness and identifying areas for improvement.
Tools for Monitoring SEO
- Google Analytics: Track and analyze website traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates.
- Google Search Console: Monitor search performance index status and identify issues affecting your site’s visibility.
- SEO Tools: Use Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz to monitor keyword rankings, backlinks, and overall SEO health.
Key Metrics to Track
- Organic Traffic: Monitor the volume of organic traffic to your website.
- Keyword Rankings: Track the rankings of your target keywords.
- Bounce Rate: Measure the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page.
- Conversion Rate: Analyze the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action on your site.
- Backlinks: Track the number and quality of backlinks pointing to your site.
Conclusion
Implementing SEO best practices from the ground up is essential for web developers who want to create search-engine-friendly websites. By focusing on SEO-friendly URL structures, optimizing on-page elements, improving technical SEO, enhancing website speed, ensuring mobile optimization, and regularly monitoring performance, you can significantly improve your site’s visibility and ranking in search engine results.
Building an SEO-optimized website is a continuous process that requires regular updates and adjustments. By staying informed about the latest SEO trends and best practices, you can ensure that your website remains competitive and effectively attracts organic traffic.